Workflow Entities Overview
Workflow Entities are the building blocks of automation workflows. Each entity represents a discrete step in message processing, with its own configuration, conditions, and scripts.
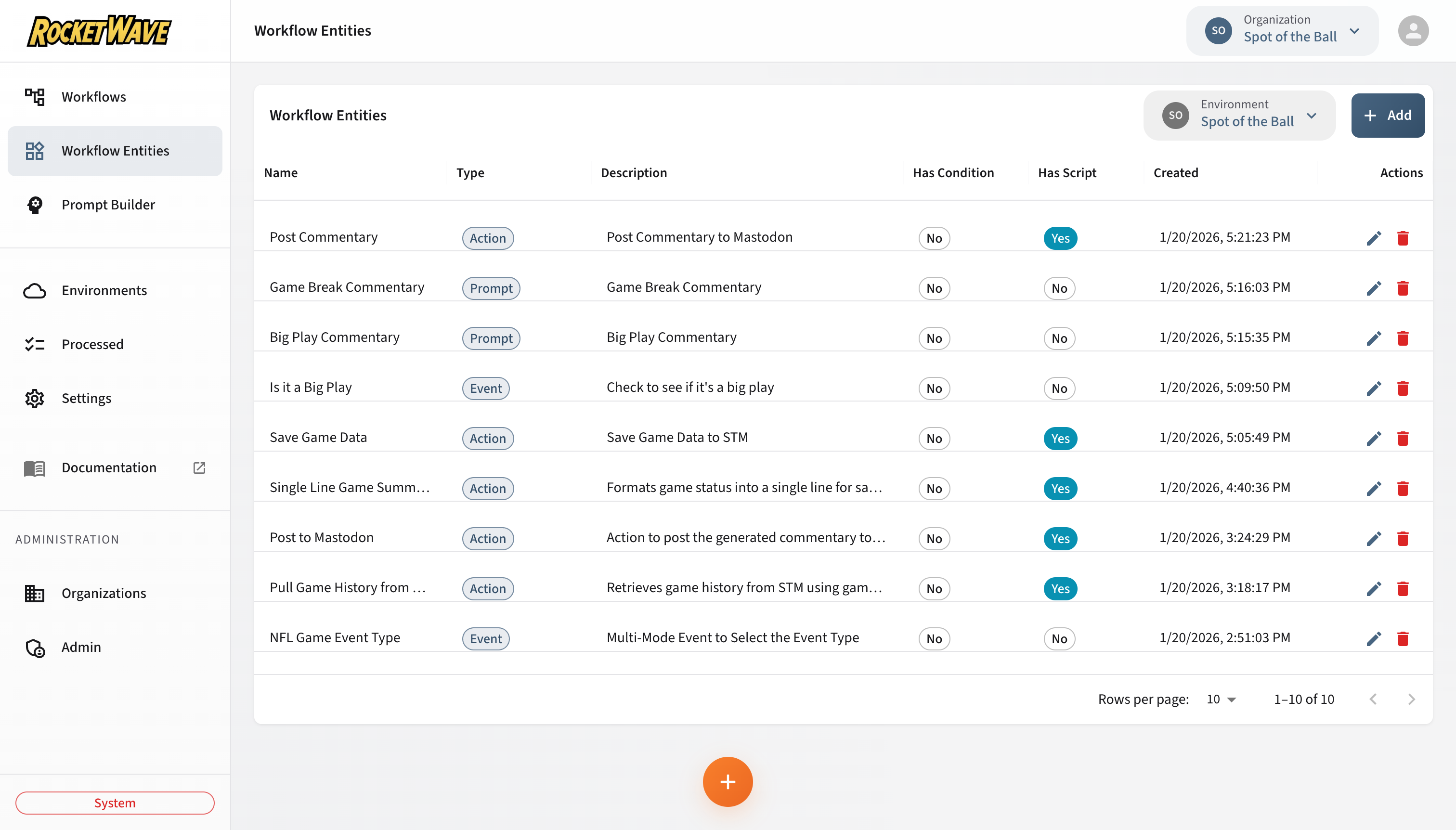
Entity Type System
The platform uses a flexible type system where each entity type defines which features are available:
| Type | Conditions | Script | Arguments | Model | Prompt | Logic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Prompt | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Action | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Entity Lifecycle
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Workflow Entity │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 1. Created in Admin UI (Workflow Entities page) │
│ 2. Associated with a Type (Event, Prompt, Action) │
│ 3. Configured with conditions, script, arguments, etc. │
│ 4. Added to Workflow Canvas (linked to a node) │
│ 5. Cached by Consumer on startup │
│ 6. Executed by appropriate Evaluator at runtime │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Common Fields
All entity types share these base fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name | string | Display name for the entity |
description | string | Optional description |
organizationId | UUID | Parent organization |
workflowEntityTypeId | UUID | Reference to entity type |
Type-Specific Features
Conditions (Event only)
A JSON tree structure for evaluating message properties:
{
"type": "AND",
"conditions": [
{
"field": "message.type",
"operator": "equals",
"value": "user.signup"
},
{
"field": "message.user.premium",
"operator": "equals",
"value": true
}
]
}
Scripts
JavaScript code executed in an isolated V8 sandbox:
// Access the incoming message
const userId = message.user.id;
// Use injected variables
const apiKey = OPENAI_API_KEY;
// Call built-in functions
print('Processing user:', userId);
// Set results for downstream entities
var ___result___ = { processed: true };
Arguments
Key-value pairs injected as variables before script execution. Arguments let you configure entities dynamically without modifying scripts.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
argumentName | Variable name that will be created (e.g., userId) |
argumentValue | Literal string or handlebar reference (e.g., {{message.user.id}}) |
argumentDescription | Documentation for the argument |
How Arguments Work:
In the Admin UI, you define name-value pairs:
| Argument Name | Argument Value |
|---|---|
eventType | {{message.event.event_type}} |
playerName | {{message.event.player.name}} |
greeting | Hello World |
At runtime, these become V8 variables:
var eventType = message.event.event_type; // → "touchdown"
var playerName = message.event.player.name; // → "Patrick Mahomes"
var greeting = "Hello World"; // literal string
Handlebar References:
Arguments wrapped in {{...}} are evaluated as expressions. Anything else is treated as a literal string:
| Pattern | Description | Example Result |
|---|---|---|
{{message.user.id}} | Extract from message | "usr_123" |
{{message.event.event_type}} | Nested property | "touchdown" |
{{___result___}} | Previous entity result | true |
{{latestPromptResponse()}} | AI response | "Generated text..." |
Hello {{name}} | Literal (no handlebars) | "Hello {{name}}" |
static-value | Literal string | "static-value" |
Use arguments to make entities reusable. Instead of hardcoding values in scripts, extract them as arguments so the same entity can be configured differently in different workflows.
Logic Branching (Event only)
Events support three branching modes:
| Mode | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Single Path | tfCondition: "Single Path" | Continue if condition passes, exit if fails |
| True/False | tfCondition: "True/False" | Branch based on boolean condition result |
| Multi | tfCondition: "Multi", logicField: "varName" | Branch based on variable value |
Model & Prompt (Prompt only)
Associate an AI model and prompt template:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
modelId | Reference to a Model (contains URL and credentials) |
prompt | Template text for the LLM (can include variables) |
Entity Execution Flow
When a message arrives, the Consumer:
- Loads Cache — All entities are pre-loaded from the database
- Matches Workflow — Finds workflows for org/environment
- Traverses Tree — Follows workflowData structure
- Evaluates Entity — Uses the appropriate evaluator:
EventEvaluatorfor Event entitiesPromptEvaluatorfor Prompt entitiesActionEvaluatorfor Action entities
- Injects Context — Message, variables, arguments
- Runs Script — Executes in V8 isolate
- Determines Next — Follows children or branches
Creating Entities
Via Admin UI
- Navigate to Workflow Entities
- Click Add
- Select entity type
- Configure fields based on type
- Save
Via API
POST /api/workflow-entities
Content-Type: application/json
{
"organizationId": "org-uuid",
"name": "Check Event Type",
"workflowEntityTypeId": "event-type-uuid",
"condition": {
"type": "AND",
"conditions": [
{ "field": "message.type", "operator": "equals", "value": "signup" }
]
},
"script": "print('Event matched:', message.type);",
"tfCondition": "Single Path"
}
Reusing Entities
Entities are reusable across workflows:
- Create once, use in multiple workflows
- Changes to an entity affect all workflows using it
- Use the Usage Count API to check dependencies before deletion
GET /api/workflow-entities/{id}/usage-count?organizationId={orgId}
Best Practices
Naming Conventions
- Use descriptive names: "Check Premium User" not "Event 1"
- Include the action: "Generate Welcome Message"
- Add context: "Post to Mastodon (Premium)"
Script Organization
- Keep scripts focused on single responsibilities
- Use arguments for configurable values
- Log with
print()for debugging - Handle errors gracefully
Condition Design
- Start with simple conditions, add complexity as needed
- Use AND/OR groups for complex logic
- Test conditions with sample messages
Related Topics
- Event Entity — Condition evaluation and branching
- Prompt Entity — AI/LLM integration
- Action Entity — Custom script execution
- Model Entity — AI model configuration
- Condition System — Detailed condition documentation
- Consumer Evaluator — Runtime execution