Settings
The Settings screen allows you to manage organization-specific configuration including Variables (secure key-value pairs), Models (AI/LLM configurations), System Models (platform-wide AI models), and Users (team member management with role-based access control).
Billing and subscription management has moved to the Dashboard for better visibility. Navigate to the Dashboard to view and manage your subscription plan.
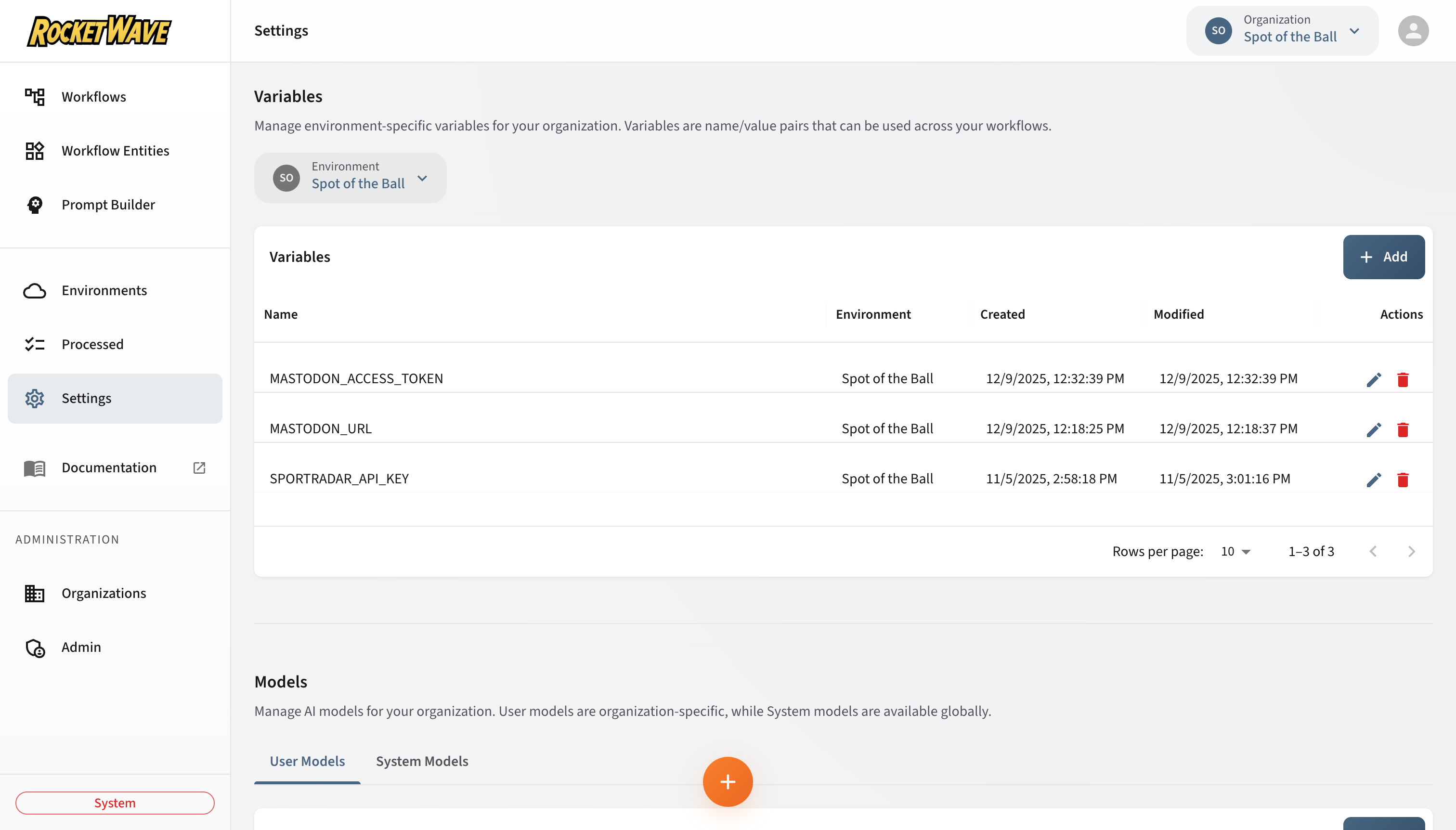
Variables
Variables are secure, environment-scoped key-value pairs that are injected into workflow execution contexts. Use variables for API keys, configuration values, and other sensitive data.
Security Model
Variables follow a write-only security model:
- Values are never exposed through the API or UI after creation
- Only the variable name is visible when editing
- Values are encrypted at rest in the database
- Values are decrypted and injected into the V8 isolate at runtime
This design ensures that sensitive credentials like API keys cannot be retrieved by users with read-only access or through API inspection.
Creating a Variable
- Select an Environment from the dropdown (required for new variables)
- Click the Add button
- Enter the variable details:
- Name (required): The variable identifier (e.g.,
MASTODON_ACCESS_TOKEN) - Value (required for new): The secret value to store
- Name (required): The variable identifier (e.g.,
Example:
Name: OPENAI_API_KEY
Value: sk-proj-xxxxxxxxxxxxx
Using Variables in Scripts
Variables are automatically injected into the V8 execution context. You can access them in three ways:
1. Direct Variable Access:
// Variables are injected as top-level vars
const apiKey = OPENAI_API_KEY;
const serverUrl = MASTODON_SERVER_URL;
2. Variables Object:
// Access all variables as an array
for (const variable of __variables__) {
print(`${variable.name}: defined`);
}
3. Variables by Name Map:
// Access variables by name from a lookup object
const token = __variablesByName__['API_TOKEN'];
Variable Table Columns
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Variable identifier |
| Environment | Which environment this variable belongs to |
| Created | When the variable was created |
| Modified | When the variable was last updated |
Editing a Variable
- Click the Edit icon (pencil) in the row actions
- Update the Name if needed
- Optionally enter a new Value (leave blank to keep existing)
- Click Save
When editing, the current value is not displayed. Enter a new value only if you want to change it.
Deleting a Variable
- Click the Delete icon (trash) in the row actions
- Confirm the deletion
Deleting a variable may break workflows that depend on it. Ensure no active workflows reference the variable before deletion.
Best Practices
Naming Conventions:
- Use
SCREAMING_SNAKE_CASEfor consistency - Prefix with service name:
MASTODON_ACCESS_TOKEN,OPENAI_API_KEY - Avoid generic names like
TOKENorKEY
Environment Separation:
Development Environment:
- MASTODON_SERVER_URL: https://mastodon.social (test server)
- DEBUG_MODE: true
Production Environment:
- MASTODON_SERVER_URL: https://your-instance.com
- DEBUG_MODE: false
Models
Models define AI/LLM service configurations for use in Prompt workflow entities. Each model stores connection details and authentication credentials.
Model Configuration
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Yes | Display name for the model (e.g., "GPT-4 Production") |
| Description | No | Optional description of the model's purpose |
| Model URL | Yes | The API endpoint URL for the LLM service |
| Authentication | Yes | Either Token OR Client Key/Secret (see below) |
Authentication Types
Models support two mutually exclusive authentication methods:
1. Bearer Token Authentication:
Token: sk-proj-xxxxxxxxxxxx
Used by:
- OpenAI API
- Anthropic API
- Most cloud LLM providers
2. Client Key/Secret Authentication:
Client Key: your_client_key
Secret Key: your_secret_key
Used by:
- AWS Bedrock (with SigV4)
- Custom authentication schemes
- Enterprise APIs with OAuth client credentials
Security
Model credentials follow the same security model as Variables:
- Credentials are write-only — never exposed after creation
- The API returns
hasToken: trueorhasClientKey: trueinstead of actual values - Credentials are encrypted at rest
- Credentials are decrypted only during Prompt entity execution
Creating a Model
- Ensure an organization is selected
- Click the Add button
- Fill in the model details:
Example (OpenAI):
Name: GPT-4 Turbo
Description: Production model for content generation
Model URL: https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions
Token: sk-proj-xxxxxxxxxxxx
Example (AWS Bedrock):
Name: Claude 3 Sonnet
Description: AWS Bedrock Claude model
Model URL: https://bedrock-runtime.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/model/anthropic.claude-3-sonnet/invoke
Client Key: AKIAXXXXXXXXXX
Secret Key: xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Model Table Columns
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Model display name |
| Model URL | The API endpoint |
| Auth Type | "Token" or "Client Key" |
| Created | When the model was created |
Using Models in Workflows
Models are selected in Prompt workflow entities:
- Create a Prompt entity
- Select the model from the Model dropdown
- Configure the prompt template
- The model credentials are automatically used during execution
// In a Prompt entity script, the model is automatically available:
// entityModel.id, entityModel.name, entityModel.modelUrl
// entityModel.token OR entityModel.clientKey/secretKey
// The built-in function handles authentication:
await executePromptWithModel();
Editing a Model
- Click the Edit icon (pencil) in the row actions
- Update name, description, or URL
- Optionally enter new credentials (leave blank to keep existing)
- Click Save
Deleting a Model
- Click the Delete icon (trash) in the row actions
- Confirm the deletion
Deleting a model will cause any Prompt entities using it to fail. Update or remove affected Prompt entities before deletion.
System Models
System Models are platform-wide AI/LLM configurations managed by system administrators. They provide a curated set of pre-configured models that all organizations can use without needing to manage their own credentials.
System vs Organization Models
| Aspect | System Models | Organization Models |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Available to all organizations | Only within the organization |
| Management | System administrators only | Organization admins |
| Credentials | Managed centrally | Per-organization |
| Use Case | Shared platform resources | Custom/private models |
Viewing System Models
System models appear in a separate grid in the Settings screen. They display:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Model display name |
| Description | Model purpose and capabilities |
| Model URL | The API endpoint |
| Visibility | Whether the model is available to organizations |
Using System Models in Workflows
When creating a Prompt entity, both system models and organization models appear in the Model dropdown. System models are labeled to distinguish them from organization-specific models.
// In a Prompt entity, the system model credentials are automatically injected
// exactly like organization models:
await executePromptWithModel();
Model Visibility Control
System administrators can toggle model visibility:
- Visible: Model appears in organization Model dropdowns
- Hidden: Model is unavailable for new Prompt entities
Hiding a system model does not affect existing Prompt entities that reference it. They will continue to work with the hidden model.
Users
The Users section allows you to manage team members within your organization with Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). User management is powered by Auth0 Organizations, providing enterprise-grade identity management.
Viewing Organization Members
The Users grid displays all current members of the selected organization:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Avatar | User's profile picture (or initial) |
| Name | User's display name from their identity provider |
| User's email address | |
| Role | User's assigned role within this organization |
| Joined | When the user was added to the organization |
Inviting New Users
To invite a new team member to your organization:
- Click the Invite button in the toolbar
- Enter the user's email address
- Select a Role for the new member (Admin, User, or Guest)
- Click Send Invitation
What happens next:
- An invitation email is sent to the specified address
- The invitee clicks the link to accept the invitation
- If they don't have an account, they'll create one during signup
- Once accepted, they appear in the Users grid with their assigned role
- They can immediately access the organization's resources based on their permissions
Invitations expire after 7 days. You can resend or revoke invitations from the pending invitations list.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
The platform implements a comprehensive permission system that controls access to resources based on user roles within each organization.
Available Roles
| Role | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| System | Full platform access (platform owners only) | Platform administrators |
| Admin | Full access to organization resources | Organization managers |
| User | Can create/edit workflows, read-only access to entities | Developers and analysts |
| Guest | Read-only access to all resources | Stakeholders and reviewers |
Permission Matrix
Workflow Permissions
| Permission | System | Admin | User | Guest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
workflows:read | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
workflows:create | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
workflows:update | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
workflows:delete | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
Entity Permissions
| Permission | System | Admin | User | Guest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
entities:read | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
entities:create | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
entities:update | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
entities:delete | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
Environment Permissions
| Permission | System | Admin | User | Guest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
environments:read | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
environments:create | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
environments:update | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
environments:delete | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
Variable Permissions
| Permission | System | Admin | User | Guest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
variables:read | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
variables:create | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
variables:update | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
variables:delete | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
Member Management Permissions
| Permission | System | Admin | User | Guest |
|---|---|---|---|---|
members:read | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
members:invite | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
members:remove | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
members:editRole | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
Special Permissions
| Permission | System | Admin | User | Guest | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
organizations:* | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | Organization CRUD (system only) |
admin:access | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | Admin screens access |
sentiment:access | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | Sentiment analysis access |
How RBAC Works
- Authentication: User logs in via Auth0
- Organization Context: User selects an organization
- Role Lookup: System queries
UserOrganizationRolefor the user's role in that organization - Permission Evaluation:
PermissionEvaluatorchecks permissions for each API request - Access Control: API routes return 403 Forbidden if permission is denied
API Permission Checking
Every API route checks permissions using the getAuthContext function:
// In API route
const auth = await getAuthContext(req, organizationId);
if (!auth.permissions.can('entities:create')) {
return NextResponse.json(
{ error: 'Forbidden: You do not have permission to create entities' },
{ status: 403 }
);
}
Database Schema
RBAC is implemented with these database models:
model User {
id String @id @default(uuid())
auth0UserId String @unique
email String @unique
name String?
picture String?
organizationRoles UserOrganizationRole[]
}
model Role {
id String @id @default(uuid())
name String @unique // 'admin', 'user', 'guest'
description String?
userRoles UserOrganizationRole[]
}
model UserOrganizationRole {
id String @id @default(uuid())
userId String
organizationId String
roleId String
@@unique([userId, organizationId])
}
Changing User Roles
To change a user's role within your organization:
- Navigate to Settings → Users
- Find the user in the grid
- Click the Edit Role button (pencil icon)
- Select the new role from the dropdown
- Click Save
Only users with members:editRole permission (Admin or System) can change roles.
Removing Users
To remove a user from your organization:
- Navigate to Settings → Users
- Find the user in the grid
- Click the Remove button (trash icon)
- Confirm the removal
Removing a user immediately revokes their access to the organization. They can be re-invited later if needed.
Auth0 Integration
The Users feature integrates with Auth0 Organizations to provide:
- Single Sign-On (SSO) — Users can authenticate with their identity provider
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) — Enhanced security for user accounts
- Social Logins — Support for Google, GitHub, and other providers
- Enterprise Connections — SAML, OIDC, and Active Directory integration
Environment Variables Required:
# Auth0 application credentials
AUTH0_SECRET=your-auth0-secret
AUTH0_BASE_URL=https://your-app.com
AUTH0_ISSUER_BASE_URL=https://your-tenant.auth0.com
AUTH0_CLIENT_ID=your-client-id
AUTH0_CLIENT_SECRET=your-client-secret
# Auth0 Machine-to-Machine credentials (for Management API)
AUTH0_DOMAIN=your-tenant.auth0.com
AUTH0_M2M_CLIENT_ID=your-m2m-client-id
AUTH0_M2M_CLIENT_SECRET=your-m2m-client-secret
API Reference
For complete API documentation with JavaScript, cURL, and MCP examples, see the dedicated API reference pages:
Variables API
| Operation | Method | Endpoint |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /api/variables?organizationId={id}&environmentId={id} |
| Create | POST | /api/variables |
| Get by ID | GET | /api/variables/{id} |
| Update | PUT | /api/variables/{id} |
| Delete | DELETE | /api/variables/{id} |
Complete Variables API Reference →
Models API
| Operation | Method | Endpoint |
|---|---|---|
| List | GET | /api/models?organizationId={id} |
| Create | POST | /api/models |
| Get by ID | GET | /api/models/{id} |
| Update | PUT | /api/models/{id} |
| Delete | DELETE | /api/models/{id} |
Complete Models API Reference →
Users & Members API
| Operation | Method | Endpoint | Permission |
|---|---|---|---|
| List Members | GET | /api/organizations/{id}/members | members:read |
| Get Member | GET | /api/organizations/{id}/members/{userId} | members:read |
| Update Role | PUT | /api/organizations/{id}/members/{userId} | members:editRole |
| Remove Member | DELETE | /api/organizations/{id}/members/{userId} | members:remove |
Invitations API
| Operation | Method | Endpoint | Permission |
|---|---|---|---|
| List Invitations | GET | /api/organizations/{id}/invitations | members:read |
| Send Invitation | POST | /api/organizations/{id}/invitations | members:invite |
| Revoke Invitation | DELETE | /api/invitations/{id} | members:invite |
| Accept Invitation | POST | /api/invitations/{token}/accept | (Invitee only) |
Roles API
| Operation | Method | Endpoint | Permission |
|---|---|---|---|
| List Roles | GET | /api/roles | Any authenticated |
Related Topics
- Variables API Reference — Complete Variables API with JavaScript, cURL, MCP examples
- Models API Reference — Complete Models API with JavaScript, cURL, MCP examples
- Environments — Create environments for variable scoping
- Prompt Entities — Use models in AI workflow steps
- Scripts Reference — Access variables in workflow scripts
- Entity API Submission — CRUD operations with permission requirements